What is a disc herniationslipped disc Biology Diagrams Anatomy of a Spinal Disc. Delving into the structure of a spinal disc, it becomes apparent that these complex components are comprised of two main parts: the outer annulus fibrosus and the inner nucleus pulposus. The annulus fibrosus is a tough, fibrous ring that provides strength and flexibility to the disc. It is primarily composed of type I

Intervertebral discs are fibrocartilaginous structures located between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae.They form a fibrocartilaginous joint between the vertebral bodies, linking them together. Collectively, the discs contribute up to one-third of the length of the vertebral column, forming an interpose between adjacent vertebrae from the axis (C2) to the sacrum.

Anatomy, Back, Intervertebral Discs Biology Diagrams
The intervertebral disc (IVD) is important in the normal functioning of the spine. It is a cushion of fibrocartilage and the principal joint between two vertebrae in the spinal column. There are 23 discs in the human spine: 6 in the cervical region (neck), 12 in the thoracic region (middle back), and 5 in the lumbar region (lower back). Lumbar Spine Anatomy The human lumbar spine typically consists of five vertebral bodies, L1 through to L5, which join with the pelvis via the sacrum at S1, and with the thoracic spine at the thoracolumbar junction (T12). The anterior longitudinal and posterior longitudinal ligaments provide additional support to these vertebral body-disc

Intervertebral Discs in Spine Anatomy. Intervertebral discs are cushion-like pads located between the bones of the spine (vertebrae). They are flat, round, and about half an inch thick. These discs have two main parts: Nucleus Pulposus: This is the jelly-like center of the disc. It contains much water, which gives the disc flexibility and helps The intervertebral disc acts as a cushion, allowing the spine to bend and twist without damaging the vertebrae. If the disc is damaged or degenerates, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and other spinal problems. Structure. The intervertebral disc is composed of two main parts: the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus.

How Many Discs Are in the Human Spine? A Detailed Overview Biology Diagrams
This review article describes anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology and treatment of intervertebral disc. The intervertebral discs lie between the vertebral bodies, linking them together. The components of the disc are nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus and cartilagenous end-plates. The blood supply to the disc is only to the cartilagenous end
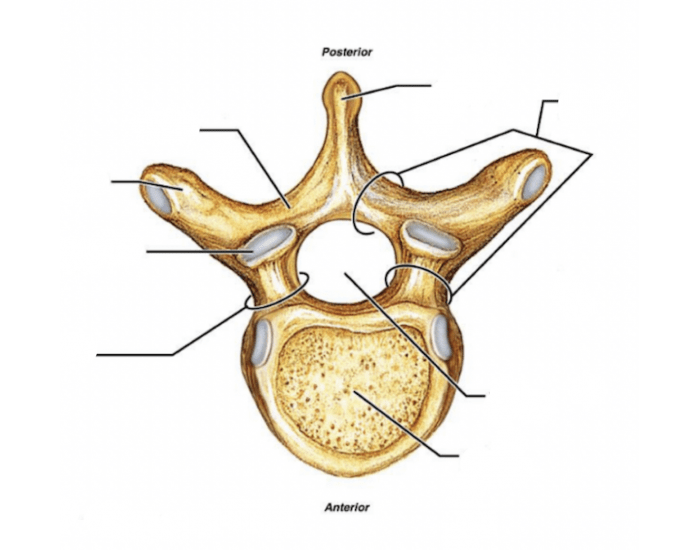
The inferior surface of the superior vertebral body articulates with the superior surface of the inferior vertebral body through intervertebral (IV) discs. These 25 discs (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, and 1 sacral) account for about 25% to 33% of the length of the spine.
